通常,工程师希望在一组实例中执行操作任务。 但是,这些任务中的许多任务需要以受控的速度进行,并在出现问题时获得反馈。 此外,管理员还通常希望确保工程师只能执行指定的操作。
“运行命令”是Amazon EC2系统管理器(SSM)的一部分,旨在让您远程和安全地管理实例。 “运行命令”提供了一种简单的方法来自动执行常见的管理任务,如运行shell脚本、安装软件或修补程序等等。 “运行命令”允许您在多个实例上执行命令,并提供对结果的可见性。通过与AWS身份和访问管理(IAM)的集成,您可以精确控制用户可以在实例上执行的操作权限。 “运行命令”执行的所有操作均由AWS CloudTrail记录,允许您审核对系统的更改。
在本文中,演示了如何执行命令来收集实例的诊断信息。 由于系统容量是按需添加,系统的容量会随时变化。为了减少实例出现意外的可能性,命令可以以受控的速度运行。 如果出现失败,您将收到通知以进行事后分析。 要确保您不会意外运行其他命令,请使用具有锁定权限的自定义操作来执行指定任务。
演练
在本节中,我将向您展示如何使用Auto Scaling设置实例,创建自定义SSM文档,然后在Auto Scaling组中的所有实例上运行命令。 同时展示了如何设置Amazon CloudWatch事件,以便在遇到问题时收到通知。
步骤1:使用Auto Scaling组启动实例
要使用“运行命令”,实例需要以下内容:
SSM代理与“运行命令”服务通信以接收命令并发送输出,并使用IAM角色授予调用服务的权限。
对于这篇文章,使用Auto Scaling组来创建一组正确配置的实例。 有关分步说明,请参阅Auto Scaling入门。
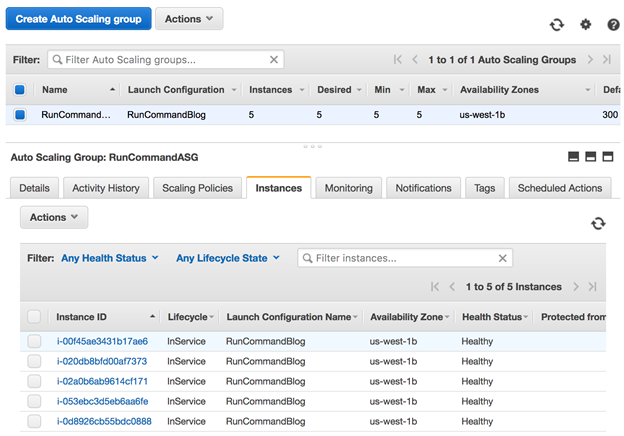
这里是一个使用了五个实例的Auto Scaling组的示例。
步骤2:创建自定义文档
“运行命令”使用文档来指定要在实例上执行的操作。文档是由JSON定义的AWS资源,它们包括您指定的步骤和参数。
AWS提供了一组执行常见任务的文档,例如运行shell脚本,配置CloudWatch,安装应用程序等。 此外,您可以为自己的文档编写特定任务。 因为IAM策略允许您控制用户被授权使用哪些文档,因此可以通过将一个指定用户限制到某个文档子集来锁定该用户可以执行的操作。
这里是一个文档的例子,它找出最消耗内存的进程。
{
"schemaVersion": "2.0",
"description": "Instance Diagnostics",
"parameters": { },
"mainSteps": [
{
"action": "aws:runShellScript",
"name": "collectInformation",
"inputs": {
"runCommand": [ "ps aux --sort '%mem' | head -5" ]
}
}
]
}
要创建自定义文档,请使用创建文档SSM API。
aws ssm create-document --name InstanceDiagnostics --content file://~/workspace/document.json --document-type Command
{
"DocumentDescription": {
"Status": "Creating",
"Hash": "92182f1392807f23556ecc3f9e1d950a575dce8e2a4b96d284b1b2fb93369db2",
"Name": "InstanceDiagnostics",
"Parameters": [],
"DocumentType": "Command",
"PlatformTypes": [
"Linux"
],
"DocumentVersion": "1",
"HashType": "Sha256",
"CreatedDate": 1492636792.396,
"Owner": "040557870006",
"SchemaVersion": "2.0",
"DefaultVersion": "1",
"LatestVersion": "1",
"Description": "Instance diagnostics example."
}
}
步骤3:设置CloudWatch事件
去年,我们在“运行命令”中添加了对命令状态更改的通知的支持。 设置CloudWatch事件通知时,您可以决定在每个实例或每个命令的基础上触发事件,并指定通知的状态。使用此功能,您可以选择在命令完成时收到通知,以进行必要的后续操作。
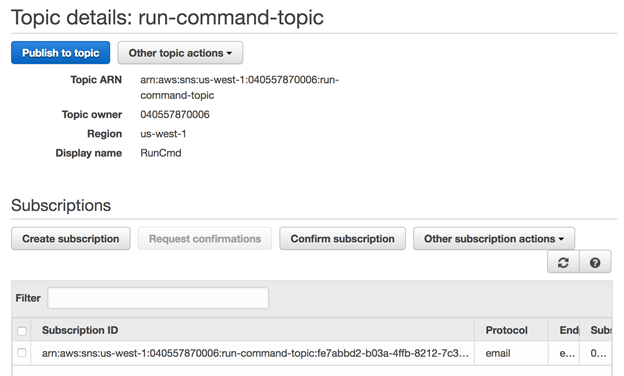
设置CloudWatch事件通知,以通过Amazon SNS通知并在命令完成时收到电子邮件。 首先创建一个在触发时发送电子邮件的SNS主题。
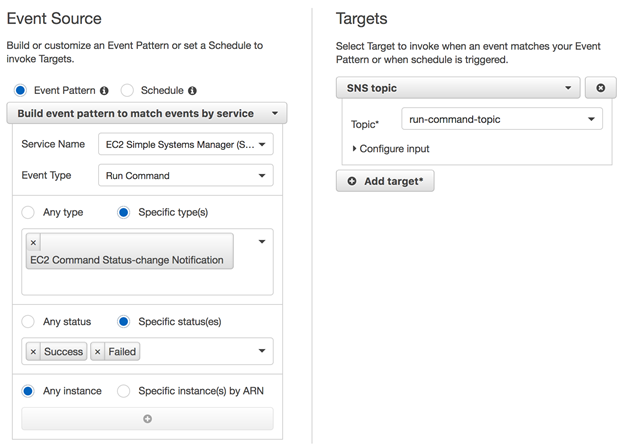
接下来,创建CloudWatch事件规则以在命令完成执行时触发SNS主题。
步骤4:测试一个实例上的命令
在将命令发送到整个实例组之前,请确保它按预期工作。
首先,检查测试实例是否正确设置并通过使用DescribeInstanceInformation API连接到该服务。 这将返回有关代理的状态、代理运行的平台以及其他实例信息。
aws ssm describe-instance-information --filters "Key=InstanceIds,Values=i-01222ecf7db201ca2"
{
"InstanceInformationList": [
{
"IsLatestVersion": false,
"ComputerName": "ip-172-31-24-177.us-west-1.compute.internal",
"PingStatus": "Online",
"InstanceId": "i-01222ecf7db201ca2",
"IPAddress": "172.31.24.177",
"ResourceType": "EC2Instance",
"AgentVersion": "2.0.755.0",
"PlatformVersion": "2017.03",
"PlatformName": "Amazon Linux AMI",
"PlatformType": "Linux",
"LastPingDateTime": 1492637593.888
}
]
}
接下来,使用先前创建的文档向上述实例发送命令。
aws ssm send-command --document-name "InstanceDiagnostics" --instance-ids "i-01222ecf7db201ca2"
{
"Command": {
"Comment": "",
"Status": "Pending",
"MaxErrors": "0",
"Parameters": {},
"ExpiresAfter": 1492645288.475,
"ServiceRole": "",
"DocumentName": "InstanceDiagnostics",
"TargetCount": 1,
"OutputS3BucketName": "",
"NotificationConfig": {
"NotificationArn": "",
"NotificationEvents": [],
"NotificationType": ""
},
"CompletedCount": 0,
"Targets": [],
"StatusDetails": "Pending",
"ErrorCount": 0,
"OutputS3KeyPrefix": "",
"RequestedDateTime": 1492638088.475,
"CommandId": "11cf0866-fdec-43a4-987b-b7a5f8ad60e9",
"InstanceIds": [
"i-01222ecf7db201ca2"
],
"MaxConcurrency": "50"
}
}
最后,检查以确保命令成功完成。
aws ssm list-commands --command-id 11cf0866-fdec-43a4-987b-b7a5f8ad60e9
{
"Commands": [
{
"Comment": "",
"Status": "Success",
"MaxErrors": "0",
"Parameters": {},
"ExpiresAfter": 1492645288.475,
"ServiceRole": "",
"DocumentName": "InstanceDiagnostics",
"TargetCount": 1,
"OutputS3BucketName": "",
"NotificationConfig": {
"NotificationArn": "",
"NotificationEvents": [],
"NotificationType": ""
},
"CompletedCount": 1,
"Targets": [],
"StatusDetails": "Success",
"ErrorCount": 0,
"OutputS3KeyPrefix": "",
"RequestedDateTime": 1492638088.475,
"CommandId": "11cf0866-fdec-43a4-987b-b7a5f8ad60e9",
"InstanceIds": [
"i-01222ecf7db201ca2"
],
"MaxConcurrency": "50"
}
]
}
步骤4:用速度控制“命令运行”
现在,您可以将命令发送到您的一组实例。
“运行命令”公开了两个新概念,用于帮助您控制发送命令的速率。 您可以通过使用max-concurrency参数来控制多少个实例同时执行该命令。 您可以指定绝对的实例数,如10,或百分比,如50%。 系统将逐步创建更多的调用(命令和实例ID配对),直到达到最大并发限制,此时它将在创建下一个调用之前等待每个当前调用完成。
第二个参数max-errors允许您指定在“运行命令”停止向其他实例发送命令之前允许的错误数。 像最大并发一样,最大错误可以指定为绝对数或百分比。
向所创建的Auto Scaling组中的所有实例发送命令,举个例子,我们指定max-concurrency为40%、max-errors为100%。 您可以使用自动生成的Auto Scaling组标签,无需任何其他工作。 通过将max-concurrency设置为40%,您可以确保命令不会同时发送到所有实例。 将max-errors设置为100%将确保所有实例都运行命令,即使某些命令调用不成功。
因为您已设置CloudWatch事件通知,所以在命令完成时将会收到通知。 “运行命令”API的输出限制为1200个字符,因此指定一个S3的位置以确保捕获完整的输出。
aws ssm send-command --document-name "InstanceDiagnostics" --target "Key=tag:aws:autoscaling:groupName,Values=RunCommandASG" --max-concurrency 40% --max-errors 100% --output-s3-bucket-name "run-command-blog" --output-s3-key-prefix "diagnostics"
{
"Command": {
"Comment": "",
"Status": "Pending",
"MaxErrors": "100%",
"Parameters": {},
"ExpiresAfter": 1492647224.49,
"ServiceRole": "",
"DocumentName": "InstanceDiagnostics",
"TargetCount": 0,
"OutputS3BucketName": "run-command-blog",
"NotificationConfig": {
"NotificationArn": "",
"NotificationEvents": [],
"NotificationType": ""
},
"CompletedCount": 0,
"Targets": [
{
"Values": [
"RunCommandASG"
],
"Key": "tag:aws:autoscaling:groupName"
}
],
"StatusDetails": "Pending",
"ErrorCount": 0,
"OutputS3KeyPrefix": "diagnostics",
"RequestedDateTime": 1492640024.49,
"CommandId": "666b0ea2-0004-4352-bddc-ac212e0e4090",
"InstanceIds": [],
"MaxConcurrency": "40%"
}
}
步骤5:验证命令结果
当命令完成后,您将收到一封电子邮件中的SNS通知。
{
"version": "0",
"id": "8bb24048-9af4-4f88-a70d-47feba9da26c",
"detail-type": "EC2 Command Status-change Notification",
"source": "aws.ssm",
"account": "040557870006",
"time": "2017-04-19T22:38:19Z",
"region": "us-west-1",
"resources": [
],
"detail": {
"command-id": "666b0ea2-0004-4352-bddc-ac212e0e4090",
"document-name": "InstanceDiagnostics",
"requested-date-time": "2017-04-19T22:38:16.105Z",
"expire-after": "2017-04-20T00:38:16.105Z",
"output-s3bucket-name": "run-command-blog",
"output-s3key-prefix": "diagnostics",
"parameters": "",
"status": "Success"
}
}
使用ListCommands API来检查总体的命令状态。 这里会返回一些信息,例如命令的状态、有多少个实例被定位(TargetCount)以及完成了多少个调用(CompletedCount)。
aws ssm list-commands --command-id 666b0ea2-0004-4352-bddc-ac212e0e4090
{
"Commands": [
{
"Comment": "",
"Status": "Success",
"MaxErrors": "100%",
"Parameters": {},
"ExpiresAfter": 1492647224.49,
"ServiceRole": "",
"DocumentName": "InstanceDiagnostics",
"TargetCount": 5,
"OutputS3BucketName": "run-command-blog",
"NotificationConfig": {
"NotificationArn": "",
"NotificationEvents": [],
"NotificationType": ""
},
"CompletedCount": 5,
"Targets": [
{
"Values": [
"RunCommandASG"
],
"Key": "tag:aws:autoscaling:groupName"
}
],
"StatusDetails": "Success",
"ErrorCount": 0,
"OutputS3KeyPrefix": "diagnostics",
"RequestedDateTime": 1492640024.49,
"CommandId": "666b0ea2-0004-4352-bddc-ac212e0e4090",
"InstanceIds": [],
"MaxConcurrency": "40%"
}
]
}
现在,您需要从指定实例收集的诊断信息。 使用GetCommandInvocation API。 这里会返回命令的输出,包括有关命令执行的更多详细信息,如开始执行时间以及执行了多久。
aws ssm get-command-invocation --command-id 666b0ea2-0004-4352-bddc-ac212e0e4090 --instance-id i-01222ecf7db201ca2
{
"Comment": "",
"ExecutionElapsedTime": "PT0.004S",
"ExecutionEndDateTime": "2017-04-19T22:13:47.122Z",
"StandardErrorContent": "",
"InstanceId": "i-01222ecf7db201ca2",
"StandardErrorUrl": "https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/run-command-blog/diagnostics/666b0ea2-0004-4352-bddc-ac212e0e4090/i-01222ecf7db201ca2/awsrunShellScript/0.diagnose/stderr",
"DocumentName": "InstanceDiagnostics",
"StandardOutputContent": "eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 02:9B:C5:26:4B:00 \n inet addr:172.31.24.177 Bcast:172.31.31.255 Mask:255.255.240.0\n inet6 addr: fe80::9b:c5ff:fe26:4b00/64 Scope:Link\n UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:9001 Metric:1\n RX packets:9905 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0\n TX packets:3260 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0\n collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 \n RX bytes:11135049 (10.6 MiB) TX bytes:514905 (502.8 KiB)\n\nlo Link encap:Local Loopback \n inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0\n inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host\n UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1\n RX packets:2 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0\n TX packets:2 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0\n collisions:0 txqueuelen:1 \n RX bytes:140 (140.0 b) TX bytes:140 (140.0 b)\n\n",
"Status": "Success",
"StatusDetails": "Success",
"PluginName": "diagnose",
"ResponseCode": 0,
"ExecutionStartDateTime": "2017-04-19T22:13:47.122Z",
"CommandId": "666b0ea2-0004-4352-bddc-ac212e0e4090",
"StandardOutputUrl": "https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/run-command-blog/diagnostics/666b0ea2-0004-4352-bddc-ac212e0e4090/i-01222ecf7db201ca2/awsrunShellScript/0.diagnose/stdout"
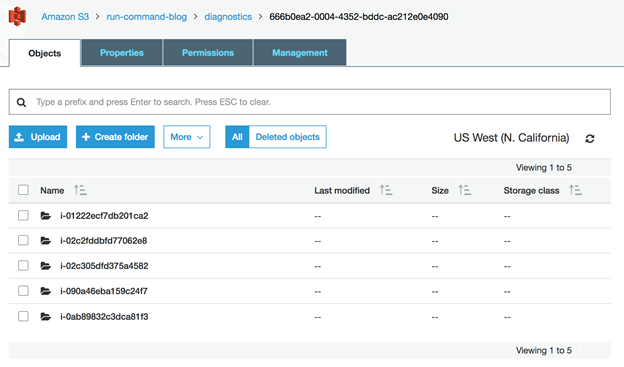
最后,因为你设置了一个S3存储桶,所有的命令调用的输出结束将保存在你指定的 S3的位置。
结论
在本文中,展示了如何使用“运行命令”以及其他AWS服务来对一组实例执行管理操作。“运行命令”提供了一种简单且可扩展的方式来管理您的实例。 您可以控制发送命令的速率,使用细粒度的权限,并使用通知来简化工作流程。

 QQ咨询
QQ咨询 阿里旺旺
阿里旺旺 #skype#
#skype#



